HTTP Live Streaming (HLS streaming), developed by Apple, was designed to replace the Flash player on iPhones. HLS is adaptive to network conditions, making it a favored protocol among streaming services. It automatically adjusts to different screen sizes and the bandwidth available on a user’s network, which enhances viewing experiences across various devices. Supported by HTML5 video players, HLS enables streaming at the optimal bitrate for a user’s connection without interrupting playback. This feature is crucial for video content, as it allows seamless scaling of video quality.
Table of Contents:
- What is HLS?
- How & Why Apple Developed HLS Encryption ?
- How does HLS streaming work?
- What is HLS Encryption? Is HLS Encryption effectively secure against piracy?
- Technical overview of HLS
- Key Benefits of HLS Encryption
- Compare HLS with other streaming protocols
- How is DRM level security for HLS Encryption possible?
- VdoCipher HLS DRM Infrastructure Details
- Demo Free Trial for HLS DRM Streaming
- FAQs
What is HLS?
HLS(HTTP Live Streaming) is a video streaming protocol used for video content across desktop and mobile devices. HLS is developed by Apple, which forms the biggest use case for the streaming protocol. Beyond Apple, there is wide support for HLS streaming across Android devices and browsers. Indeed, HLS can be used as a streaming protocol for all major browsers, including Chrome and Firefox.
In HLS Encryption the video files are encrypted using a secure AES-128 algorithm. The AES 128 encryption is the only publicly available security algorithm that is used by the NSA for encrypting its top-secret classified information.
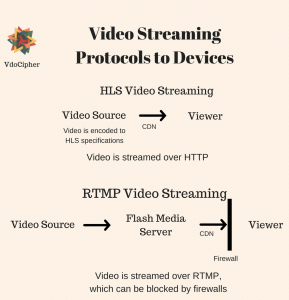
HLS streaming and HLS Encryption can be used for both the cases of live streaming and for Video on Demand streaming (VOD). Because video streaming is over HTTPS, there is no need for a streaming server, unlike RTMP, which requires its own streaming server.
How & Why Apple Developed HLS Encryption ?
Until about 2010, Flash was the most popular video streaming application. It was supported by all desktop browsers. Because Flash utilized the same runtime across all browsers, it meant that video streamers did not have to create separate workflows for different devices. DRM and encryption were also supported by Flash.
Flash was however plagued by security issues. Video playback on Flash was processor-intensive, which caused phone overheating & mobile batteries to drain very fast. For these reasons Apple did not support Flash in the iPhone and in iPad, instead including support for native HTML5 video playback.
Apple created its specifications for video streaming, which could by both live streaming platforms and for pre-recorded video streaming platforms. Android OS followed suit by blocking flash playback from browsers on Android. From the introduction of the smartphone to the emergence of MPEG-DASH around 2015, Apple’s HLS streaming has been the most widely used protocol. You cab experience uninterrupted broadcasts with M3U8 live streaming, the go-to format for live video delivery.
Because of Apple’s continued support for the protocol, encoding for HLS player is an integral element of any video streaming provider’s workflow like Google cloud video streaming.
Explore More ✅
VdoCipher empowers course creators, film makers and trainers with multi-DRM protected video streaming, ensuring piracy protection and smooth playback globally.
How does HLS Encryption work?
In plain vanilla HTML5 video streaming, only a single video file is available for streaming. The download of the complete video file is initiated every time the stream is played. Even if a viewer watches only 2 minutes of a 30-minute video, the full video would be downloaded, causing data wastage at both the server and the user end.
Streaming protocols remove this inefficiency in video streaming. Streaming protocols such as HLS effectively break down a video file into multiple chunks when streaming, and these video files are downloaded over HTTP in succession.
HLS streaming uses the same workflow for both live and for on-demand content. The core idea in multi-bitrate streaming is that multiple renditions of each video, of varying resolution, are encoded. High-resolution videos are delivered to large screen devices having high network bandwidth, whereas lower-resolution videos are encoded for mobile phones. Encoding for low resolutions also ensures continuous video streaming when the network connection speed drops.

When the user decides to change video resolution, or when the network bandwidth changes, video streams can be manually (or automatically) switched. HLS video streams are encoded using the H.264 standard, which can be played across all devices. Each of the video copies is broken into multiple chunks having the .ts (transport stream) extension.
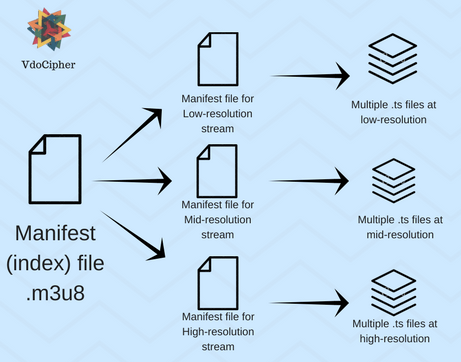
There is a main index file, called the manifest file (.m3u8 file format), associated with the video stream. The main manifest file contains links to the specific manifest files associated with each unique video stream. Each of these specific manifest files in its place directs the video stream to the correct URL for video playback when streams are switched. This ensures that stream switching is seamless. This process of a manifest file referring to the video stream is the same for both live video streaming and for on-demand video streaming.
The only difference for live video is simply that the video files are being encoded in real time. These m3u8 files can be played with M3U8 player is a simple video player application that can play any valid online video URL. It is capable of playing m3u8, mp4, HLS and many more supported video links from the internet
Streaming over HTTP has many advantages over using a separate server. For example, firewalls that may be used to block ports used for RTMP are unlikely to affect video streaming over HTTP. No additional costs are required for streaming over an HTTP server. M3U8 live streaming offers a reliable solution for broadcasting real-time events to a global audience.
Here’s how HLS works, step by step:
- Encryption of Video Segments:
- HLS encryption works by encrypting each video segment (chunk) using a symmetric key algorithm, typically AES-128 (Advanced Encryption Standard).
- The encryption is applied to each segment independently, ensuring that only users with the proper decryption key can access and view the content.
- Key Distribution:
- The encryption key used to secure the video segments is typically stored on a separate, secure server.
- The HLS playlist (m3u8 file) includes a reference to the location of the encryption key, but not the key itself, to ensure that only authorized clients can retrieve the key.
- Secure key exchange mechanisms, often facilitated by HTTPS, are used to deliver the key to the authorized client.
- Decryption by the Player:
- When a viewer accesses the video stream, their video player fetches the encryption key using the URL provided in the playlist.
- The player then uses this key to decrypt the video segments as they are downloaded, allowing for real-time playback of the content.
Mobile Video Streaming Using HLS Protocol
When users upload a video to a server, it undergoes several phases of processing. Initially, the video is encoded in various resolutions and then segmented into containers, where each segment is indexed in the M3U8 format. This index file is crucial as it is hosted on a server and accessed by mobile applications to retrieve video chunks.
Server Components
Key elements of the server include the encoder and segmenter. The encoder receives the input stream during video upload and encodes it into different formats such as H.264 + MP3 and MPEG-2, creating multiple output streams. These streams are then passed to the segmenter, which divides them into video chunks and generates corresponding index files. Each stream has its distinct index file.
M3U8 File Format
The M3U8 file format is essential for indexing multimedia files. It contains pointers to the locations of video files saved with a .ts extension. These index files are generated by the segmenter and also specify the duration of video chunks, typically set to 10 seconds. They enable dynamic switching between video streams depending on the user’s network bandwidth. The client software autonomously decides the optimal times to switch streams based on network conditions. You can direct your viewers to your live content with an M3U8 streaming URL, making access to your streams straightforward and efficient.
Mobile Application Interaction
Mobile applications retrieve the M3U8 index file from the server, which directs them to the required video streams. The application downloads these streams in a sequential manner, and playback begins once enough segments are buffered. As one index file is exhausted, the application proceeds to scan the next until the ‘endlist’ tag is reached.
System Implementation
The development of the mobile application is geared towards enabling users to share videos seamlessly. Users upload videos, which are then encoded and segmented by the HLS server into streamable video slices saved in .ts format. Index files in M3U8 format are generated and uploaded to a storage database. When a user wishes to watch a video, the application sends a request to the server to retrieve the video through the storage, ensuring that the video plays smoothly on the device’s native media player API.
In conclusion, HLS protocol facilitates the streaming of high-quality videos that adapt to varying network conditions. By managing video segments through a manifest file, the mobile application ensures that users can access the best possible video quality based on their current network environment, providing a robust and uninterrupted streaming experience.
What is HLS Encryption? Is HLS Encryption effectively secure against piracy?
HLS encryption involves securing the video segments delivered via HLS to prevent unauthorized access, piracy, and content theft. The encryption process ensures that even if a malicious actor intercepts the video stream, the content remains unreadable without the correct decryption keys.
HLS AES-128 encryption refers to video streams using HLS streaming protocol wherein the video files are encrypted using the AES-128 algorithms. The key exchange happens through the secure HTTPS protocol. If done in a rudimentary way the key for decryption can be seen from the network console by accessing the manifest file. A poor implementation of HLS encryption would result in plugins automatically finding the key and decrypting the HLS encrypted stream, rendering video security ineffective.
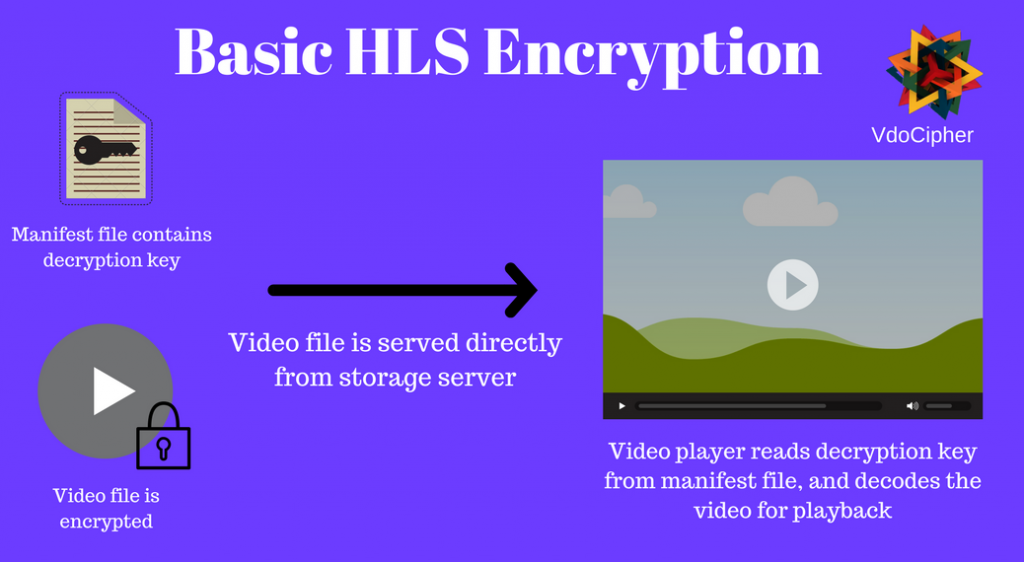
There are however methods to strengthen the HLS Encrypted stream. The challenge is to make sure that the key is not exposed directly. These are the options for additional security in HLS Encryption:
- Not including URL to decryption key in Manifest File
Implementations for this vary widely, and are quite difficult by themselves. This method for protecting HLS content may also cause compatibility issues on devices. If done properly however it is definitely a major improvement in video security.
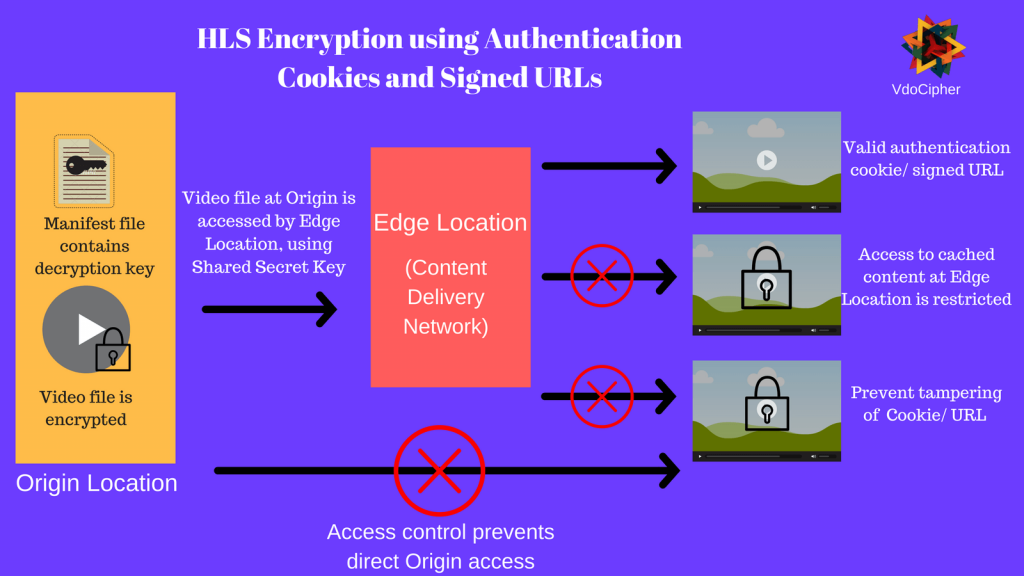
- Using authenticated cookies for HLS Encryption streaming
In this method, the browser of authorized users stores authentication cookies. These cookies are stored with a digital signature, to ensure that they are not tampered with. This ensures that only the authorised user (and not some external plugin) is seeking to fetch content. The following workflow is used for configuring authentication cookies for HLS encryption:
- Trusted signers are configured, who have permission to create authentication cookies. This configuration is done at the edge location (content delivery network)
- Application is developed to send set-cookie headers to authorized viewers
- Authorized users store name-value pairs in the cookie
- When user requests protected content, the browser adds the name-value pair in the cookie header to the request
- The video CDN uses the public key to verify the digital signature in the name-value pair
- If the authentication cookie is verified, the CDN looks at the authentication cookie’s policy statement. The policy statement determines if the access request is valid. For example, the policy statement could include the beginning and end time for cookie validity.
For further information on authentication cookies for content protection, you can have a look at Amazon Cloudfront’s documentation.
- Signed URLs can be generated for authorized users
The following workflow is used for configuring signed URLs for HLS encryption:
In the CDN trusted signers are created, who have permission to create signed URLs
- Develop an application to create signed URLs for protected content
- When user requests protected content by signed URLs, the application verifies if they have the authorization to access it
- If verified, the application creates a signed URL and sends it to the requesting user
- On accessing content through a signed URL, the CDN verifies that the URL has not been tampered with. This is done by using the Public Key to verify the digital signature of the URL
- If the signed URL is valid,
- The CDN uses the public key to verify the digital signature in the name-value pair
- If the signed URL is verified, the CDN looks at the signed URL’s policy statement. The policy statement determines if the access request is valid. For example, the policy statement could include the beginning and end times for the signed URL. For protecting content, this period of validity of URLs should be short – as little as a few minutes is optimal. For this you can create dynamic URLs, that change every few minutes.
For further information on signed URLs for content protection, you can have a look at Amazon Cloudfront’s documentation.
All these 3 steps make the video stream considerably immune to direct download through plugins. However, these methods are still breakable by already available codes and tech hacks.
Technical overview of HLS Streaming
HLS streaming or HTTP live streaming is a video streaming protocol to stream audio and video across all major browsers and devices. Here’s a brief overview of how HLS Streaming works.
Source and Encoding: Video content can be either live or recorded and is first encoded into all the relevant formats and quality. The video is also compressed to ensure it can be streamed easily, as raw files are usually pretty big.
Segmentation and Multiple Formats: After the encoding is done the video is further split into segments of about 10 seconds each. Segmentation makes it easier to switch between video quality, this is done dynamically based on the user’s internet speed.
Creation of M3U8 Playlist: An M3U8 playlist file is created, which contains information about the video segments of all the different qualities. It guides the player to pick the right segment based on internet speed.
Delivery and Adaptation: All the video chunks and the m3u8 playlist are saved on an HTTP server. When someone streams the video, the m3u8 playlist is downloaded and the video chunks are downloaded. As the internet speed changes, the player chooses the higher or lower-quality video chunks based on it. It ensures a smooth viewing experience with minimal buffering.
Key Benefits of HLS Streaming
Here are the key benefits of HLS (HTTP Live Streaming):
Compatibility: HLS is compatible with almost all browsers and devices. Initially HLS was limited to Apple devices now it has a much broader range browser it supports.
Adaptive Streaming: HLS ensures a smooth viewing experience by scaling the video quality. It does this based on the user’s internet speed, the quality scales up or down based on the internet speed. This ensures that there is no buffering at lower speeds.
Live and On-Demand: HLS works for both live and recorded streaming. This makes it pretty versatile for streaming different types of content.
Security: HLS uses AES-128 encryption to encrypt the video chunk, to protect videos from unauthorized access. HLS encryption significantly reduces the risk of content theft and piracy. Unauthorized viewers cannot access or view the content without the encryption key.
Scalability: HLS offers good scalability to deliver live and record content across global CDN. These CDNs distribute the streaming load among various servers. This distribution strategy efficiently handles sudden increases in viewers, such as unexpected large live audiences, ensuring a stable streaming experience.
Compare HLS with other streaming protocols
Comparing HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) to other video streaming protocols:
MPEG-DASH:
MPEG-DASH is similar to HLS in providing adaptive bitrate streaming. But MPEG-DASH is more flexible with different codecs and containers. HLS is more widely supported, especially on Apple devices. MPEG-DASH is gaining popularity due to its open standard nature.
RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol):
RTMP is older and great for low-latency streaming, like live broadcasts. However, it doesn’t support adaptive streaming and is less compatible with modern devices. HLS, while having slightly higher latency, offers better device compatibility and adaptive streaming.
Microsoft Smooth Streaming:
This is Microsoft’s version of adaptive streaming. It works well with Microsoft devices and software. However, HLS has wider support across various platforms and devices compared to Microsoft Smooth Streaming.
HDS (HTTP Dynamic Streaming):
HDS is Adobe’s streaming protocol. It’s similar to HLS in adaptive streaming but is less common. HLS has broader support and is more widely used than HDS.
How is DRM level security for HLS Encryption possible?
DRM requires that the key exchange and licensing mechanism is highly secure and is always out of reach of external tools and hackers. A DRM technology also has additional elements. It delivers a license file, which also specifies the usage rights of the viewer. Usage rights specify the conditions in which the video playback is allowed.
Implementation of these usage rights ensures that the signed key used for decryption can only be used for playback on the viewer’s device. The key would simply fail to decrypt the video stream if the video file is copied to any other device.
DRM adds complex layers of workflow for license management. This workflow includes:
Specifying highly detailed usage rights such as
- Limiting video playback on a device to only a fixed number of times
- Video access can expire after a period of days if the subscription is not renewed
- Limiting the device or screen on which the video can be played. For example usage rights can be used to restrict users to cast their video playback on an external device such as a Smart TV.
The license database is also bound to the user’s device, which means that if shared the license and decryption key becomes redundant.
Licenses are also signed with the digital signature, which means that they cannot tamper with either during transit over HTTP or when stored locally on the device.
Implementing DRM along with HLS streaming entails considerable modification of the HLS Encryption infrastructure. At VdoCipher, we have been able to do that and provide a full-fledged proprietary + HLS DRM. We cannot technically say that we are streaming an HLS encrypted stream as it is highly modified. We use a combination of other technologies based on different platforms and are able to roll out a cross-device, cross-browser compatible DRM.
VdoCipher HLS DRM Infrastructure Details
- Upload of Videos (All common formats are supported )
The content can be uploaded through Dashboard or APIs. Upload from desktop, FTP, DropBox, Box, URL, Server all is supported. - Encryption & Transcoding for DRM streaming
Videos are converted into encrypted files, and multiple qualities & versions for ensuring delivery of quality content at all devices, browsers, and all connection speeds. The encrypted content is stored at our AWS S3 servers and raw videos are never exposed. We have set up our custom EC2 instances for the encoding pipeline, and the resultant files are hosted securely on AWS S3 servers. - Encrypted Video Streaming (Modified HLS Encryption & Streaming)
As discussed above the high-security key and license exchange mechanism supports the transfer of encrypted video data, ensuring HLS DRM level security. Dynamic URLs ensure that each playback is authenticated and the URL cannot be extracted outside the website or app for pirated playback. We use multiple top tier CDNs – Cloudfront, Akamai, Google CDN, Verizon to ensure smooth delivery of content all across the globe - Decryption in Video Player & Watermarking
There is a private communication between our API & the client website. This ensures that its not possible for hackers to decrypt our streams. The One Time encryption that we use is theoretically and practically hack-proof. The website embedding the video content requests a One-time password from the VdoCipher web server using the API. This OTP request is made only after the user is authenticated. The VdoCipher API returns the OTP, which is used to render the embed code. This embed code is valid for a single playback session only. Along with the key a usage policy is specified, ensuring that only a logged-in and authenticated user is allowed to playback the encrypted video. The video would simply fail to play if an external plugin or downloader is used to try to access the video file.We have timely modifications to our licensing and authentication mechanism to keep security updated. - Watermarking
Video licensing and playback are combined to generate customisable viewer specific watermarks. The watermark can be IP address, Email ID and User ID shown in customisable colour & transparency to identify a playback session by the viewer. - Result – Progressive High Secure Streaming
Through this 6-step Video Hosting, Encryption and Streaming process, VdoCipher, as a video hosting software, is able to provide a progressive high security video streaming with future buffer possible. This is also different from RTMP which does not maintain any buffer and can be quite erratic as a result.
You can find out more about DRM Solution here.
Demo Free Trial for HLS DRM Streaming
You can signup for a free full version trial at VdoCipher.
Online businesses also often require features over and beyond video security. VdoCipher fulfills all major requirements for enterprise video hosting. The complete set of features that VdoCipher offers for enterprise video hosting may be found here.
Also, do read our blog on react native video playback.
FAQs
Is HLS DRM protected?
HLS is not protected with DRM by default. Traditionally, HLS streams could only be protected using Apple FairPlay DRM but with new updates, HLS can be protected by Google Widevine DRM in addition to Apple FairPlay DRM.
Is HLS unicast or multicast?
Traditionally, HLS was designed by Apple for Quicktime, Safari, and iOS devices. It did not used to support multicast but with new updates HLS, has emerged as the de facto multicast format for live streaming and video on demand (VOD).
Is HLS better than RTMP?
Moreover, it depends on the use case but HLS has notable advantages which include embedded closed captions, good advertising standards support, synchronized playback of multiple streams, and DRM support. RTMP has advantages of low latency, flexibility, efficient bandwidth usage, and dynamic content delivery.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.




Leave a Reply