Streaming piracy has become the dominant way people consume movies, TV shows, and live events and unfortunately, it’s also at the heart of a global piracy epidemic. “Pirate” streaming services and illicit live streams now account for the majority of online piracy, undermining legitimate platforms and costing the media industry tens of billions in lost revenue. This comprehensive look at streaming piracy will shed light on its scope and scale, the technical methods pirates use. Real-world examples of piracy in action, the legal implications of these activities, and the technical countermeasures, including secure streaming solutions like VdoCipher that can help fight back.
Table of Contents:
- The Scale of Streaming Piracy Today
- Why Do People Turn to Pirate Streaming?
- Regional Streaming Piracy Breakdown: Piracy in the U.S., India, and EU
- Risks and Consumer Harms of Pirate Streaming
- Protecting Streams: Technical Countermeasures Against Streaming Piracy
- VdoCipher: Hollywood-Grade Video Security for Premium Video Content
- FAQs
The Scale of Streaming Piracy Today
Online piracy is no longer limited to file downloads or bootleg DVDs, it has largely shifted to streaming. The numbers are staggering. Consider these facts about the scope of streaming piracy:
- Hundreds of Billions of Views – Pirated video material receives over 230 billion views worldwide each year. Incredibly, that means illicit streams attract a viewership rivaling or exceeding legal platforms.
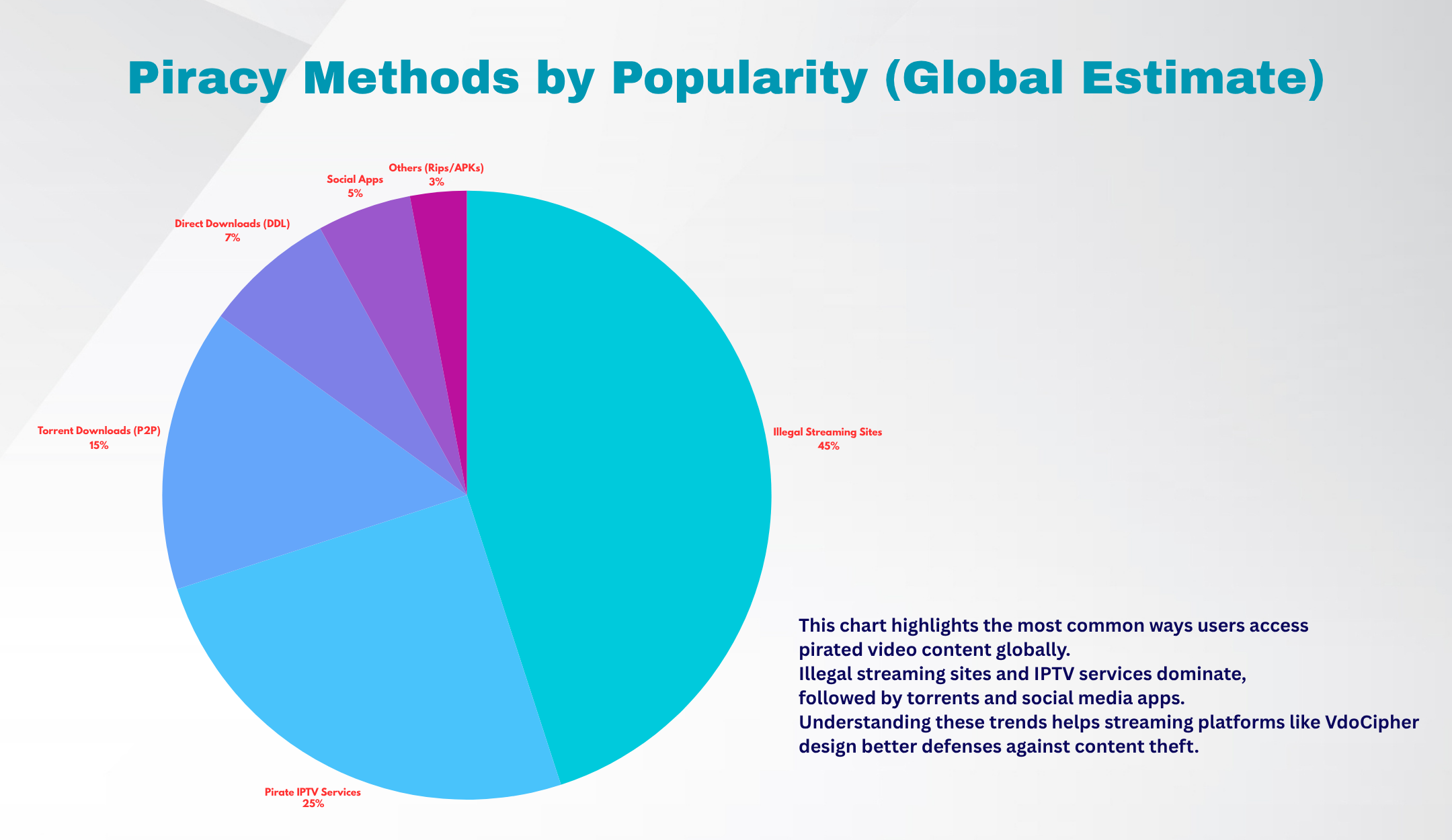
- Streaming is 80% of Piracy – An estimated 80% of all online piracy is now conducted via illegal streaming services, rather than downloads or torrents. In other words, streaming has become the go-to method for pirates.
- Surging Traffic to Pirate Sites – In 2023, visits to piracy websites topped 229 billion, up 6.7% from the previous year. This growth shows piracy isn’t slowing down, it’s increasing despite the proliferation of legal streaming options.
- Massive Economic Losses – Analysts project that streaming piracy will cost U.S. video providers over $113 billion in lost revenues by 2027. Already, around $30 billion per year is estimated to be lost in the U.S. due to piracy, with 80% of those losses attributed to streaming theft. Globally, the film industry alone loses on the order of $40-97 billion annually from digital piracy.
- Widespread User Participation – Millions of people knowingly or unknowingly use pirate streaming services. In the U.S., about 9 million broadband subscribers are paying for illegal on-demand TV or IPTV services.
These statistics paint a stark picture. Streaming piracy is a mainstream phenomenon, not a fringe activity. Virtually every popular film or show is available illicitly, often the same day it’s released. Live sports events, from boxing matches to soccer finals, draw millions of unauthorized viewers via pirate streams. The result is a multibillion-dollar black market that undermines legitimate streaming services and threatens the livelihood of content creators.
Why Do People Turn to Pirate Streaming?
It’s worth asking, if legal streaming services are widely available, why do so many people still resort to pirate streams? Several factors drive the ongoing allure of streaming piracy:
Cost and Subscription Overload
Keeping up with all the shows and sports you want often means juggling multiple paid subscriptions. Netflix, Disney+, Amazon, sports league passes, etc. Many viewers feel frustrated by rising costs and fragmented content across platforms. Illegal streams offer a tempting “all-in-one” solution for free or a token price. As Netflix itself warned investors, pirate services offer “virtually all content for free,” undercutting the value of legal streaming. In some cases, easy access to pirated content has even driven higher piracy rates as consumers balk at subscribing to numerous services.
Every minute, your premium content could be leaking onto pirate platforms.VdoCipher gives you the same anti-piracy tech trusted by Netflix. Hollywood-grade DRM, dynamic watermarking, and real-time analytics to trace and block content theft.
Convenience and Availability
Pirate streaming sites and apps can be extremely user-friendly, providing on-demand access to vast libraries of movies, series, and live channels in one place. Some illicit applications mimic the interface of legitimate platforms, making it simple for a non-technical user to find what they want. If a movie or live game isn’t available legally in a user’s region (due to release delays or geo-blocking), pirates rush to fill that demand instantly.
No Perceived Penalty
Historically, viewers of illegal streams have felt there’s little chance of getting caught or punished. There’s a misconception that “streaming isn’t as bad as downloading” or that it exists in a legal gray area. This false sense of security, coupled with anonymity tools like VPNs, means many users don’t fear legal repercussions.
Content Exclusivity and FOMO
Sometimes highly anticipated events (a championship match, a blockbuster movie premiere) are behind expensive paywalls or exclusive to certain regions. Pirates capitalize on fans’ fear of missing out by restreaming that content freely. For instance, when a major boxing or UFC bout is offered only via costly pay-per-view, countless unauthorized feeds will pop up on social media or IPTV services so fans can watch without paying.
In short, piracy often wins on price and convenience. Unless the legal offerings match that convenience at a fair price point, a segment of consumers will always be tempted by the “free” alternative, despite its illegality and other risks.
Regional Streaming Piracy Breakdown: Piracy in the U.S., India, and EU
United States
The United States sees enormous losses and high user engagement in streaming piracy. Digital piracy costs American businesses an estimated $77 billion per year, and about 80% of U.S. piracy is attributed to illegal streaming of video content. This reflects both the scale of the U.S. media market and the popularity of pirate streaming sites/services among U.S. consumers.
A study found U.S. online TV and film piracy led to annual losses between $29.2 billion (conservative) and $71 billion, along with 230k-560k lost jobs each year. By 2024, with the growth of streaming, the upper end of that range ($71B) has effectively become the baseline in some estimates. User behavior surveys confirm that piracy is widespread in America.
In 2024, over one-third of U.S. adults (around 33%) admitted to pirating TV shows or movies in the past year. In fact, nearly 50% of Americans have pirated video content at least once in their lives. On average, the U.S. “Casual pirate” will illegally stream or download about 2 shows or movies per month, meaning most people still consume legal content as well, but supplement with a couple of pirated titles. (Notably, 80% of those who pirated in the last year also pay for two or more legal streaming services, indicating that many pirates are trying to fill gaps in legal offerings or avoid additional fees.) Certain content is especially popular in U.S. piracy: recent surveys show that the most pirated items include current TV series, movies still in theaters, and exclusive originals from platforms like Netflix.
One analysis estimated that 126.7 billion viewing instances of the U.S, produced TV episodes are pirated each year (globally), a staggering number that highlights the global demand for American TV content via illicit means.
Consulting firm Parks Associates projects that U.S. video providers will lose a cumulative $113 billion to piracy and password sharing from 2022 through 2027.
India
India has one of the highest rates of content piracy in the world, despite the rise of affordable streaming platforms. A comprehensive 2024 report by EY and IAMAI revealed that 51% of Indian media consumers access content from pirated sources, more than half of the audience! This rampant piracy spans movies (via camcording and illicit copies) and OTT streaming content. The “piracy economy” in India was valued at ₹224 billion in 2023 (approximately $2.8–3.0 billion USD), which is equivalent to the fourth-largest segment of India’s M&E (Media & Entertainment) industry. The losses include about ₹137 billion from pirated film content (e.g. illegal recordings of theatrical releases) and ₹87 billion from piracy of OTT streaming content. The government also loses out, an estimated ₹43 billion in tax (GST) revenue is lost due to the black-market nature of pirate services.
Piracy methods in India
Streaming is the dominant mode here as well. 63% of pirated content consumption in India is through streaming sources. (e.g. pirate streaming sites or IPTV apps), followed by mobile apps distributing unlicensed content. Torrenting and direct downloads exist but are relatively less common compared to illicit streaming in the Indian context. Notably, messaging platforms and social media have become piracy hubs in India.
For example, Telegram is widely used to share pirated videos and courses (more on education piracy below). These losses come despite a 150% increase in legitimate streaming subscription revenues in recent years, indicating that even as more Indians pay for Netflix, Hotstar, Amazon Prime, etc., a huge segment continues to consume pirated media. Enforcement has been challenging, and consumers often cite the cost of multiple subscriptions or delayed availability of content as motivations for piracy. However, awareness is growing. The EY/IAMAI report noted that 62% of those who pirate content in India agree that stricter legal enforcement is needed to curb the problem.
Europe (EU)
Across the European Union, digital piracy remains widespread and stubbornly persistent. A 2023 study by the EU Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) found that Europeans accessed pirated content about 10 times per month on average. In some EU countries, the frequency is even higher, for example, consumers in the Baltic states and Cyprus averaged over 20 piracy site accesses per month, while Italy had the lowest rate around 7.3 per month. In other words, despite years of anti-piracy initiatives, the typical European internet user is still visiting pirate sites regularly (roughly 10 times monthly). The EUIPO expressed alarm that there has been no overall decrease in piracy usage, and in fact certain types (like TV and sports streaming) are on the rise.
In Europe, TV shows are the most pirated content, accounting for roughly half of all illicit accesses. The EUIPO data shows a monthly average of 5 illegal TV streaming views per user in the EU. Publishing (e.g. e-books, manga) and music piracy still occur, but film piracy has declined somewhat in Europe (partly due to more VOD availability). Crucially, streaming sites are the preferred access mode in Europe as well. Streaming (including illegal IPTV) comprised 58% of piracy in the EU, versus nearly 32% via direct download or torrent methods.
Live sports streaming piracy is sharply climbing in Europe, EUIPO noted a 30% increase in live sports piracy from 2021 to 2022. By 2022, Europeans averaged about 0.55 illicit sports streams per month, up from 0.42 a year earlier. This reflects the growing popularity of watching soccer, rugby, Formula 1, etc. through unauthorized streams. Another concerning trend is the growth of illegal IPTV subscriptions in Europe. Pirate IPTV services (which offer bundles of live TV channels, sports, and on-demand content for a cheap fee) have gained traction. The EUIPO study estimated that up to 1% of EU internet users had subscribed to an illegal IPTV service by 2023 (excluding those who subscribed prior to 2022)
While 1% may sound small, across the EU’s population this translates to millions of subscribers paying pirate providers instead of legitimate TV operators. And that figure was the incremental uptake in just two years, suggesting the true total (including long-time pirate subscribers) is higher.
Unlike the U.S. and India, the EU doesn’t often quote a single “loss” figure, but the impact is clearly significant. One study some years back estimated that illegal TV services in the EU generate around €1 billion a year in illicit revenue (displacing money from legal pay-TV). The EU’s creative industries have lobbied for stronger enforcement as piracy continues to dent revenues for broadcasters, sports leagues, and content producers. Countries like Germany and Italy have relatively lower piracy rates (due to better legal alternatives and enforcement), whereas Eastern Europe and Southern Europe have .
Other Notable Regions
Asia-Pacific and Developing Markets
Piracy rates are also notoriously high in parts of Asia (outside India) and the Middle East/North Africa. For instance, consumer surveys have found Indonesia, Egypt, Vietnam, and the Philippines among countries with a large share of users pirating content regularly. These regions often have limited legal options or lower incomes, making pirated content more attractive. In Africa, a survey across several countries found tens of millions of visits to top piracy sites within a few months, indicating a substantial user base.
Latin America
Countries like Brazil have significant piracy issues; Brazil has conducted large anti-piracy operations (like “Operation 404” targeting pirate sites). A 2022 survey in Mexico found about 50% of consumers had used pirated streaming or pay-TV services – similar to rates in Asia. Live sports piracy (especially for soccer) is very common in Latin America as well.
Global South vs. Global North
Interestingly, some data suggests piracy is flattening or even decreasing in some developed markets (with plentiful affordable streaming options), while it rises in emerging markets where legal content is still comparatively expensive. But the global connectivity and content demand mean piracy is truly a worldwide phenomenon – popular U.S. or UK shows are pirated in huge numbers in every country where they aren’t readily available or are behind a paywall.
Risks and Consumer Harms of Pirate Streaming
Before comparing legal vs. pirate services, it’s important to highlight that pirating content isn’t a “victimless” activity. Not only does it harm industries, it also exposes consumers to significant risks. A recent study demonstrated the personal risks of using pirate streaming sites or services:
Financial fraud – Nearly 72% of consumers who paid for pirate streaming subscriptions with a credit card experienced subsequent fraudulent charges, compared to only 18% of those who never use pirate sites. In other words, many pirate IPTV or streaming sites are linked to credit card theft or scams. These illicit operators often sell user data or abuse payment info.
Malware and identity theft – 44% of people who frequently used piracy apps/sites became victims of identity theft, vs only 10% of non-pirating users. Piracy sites are notorious for spreading malware that can steal personal data or infect devices. Users of illegal streams may unknowingly download ransomware or keyloggers. The Digital Citizens Alliance report “Giving Piracy Operators Credit” (June 2023) underscores how pirate streaming hubs double as hubs for cybercrime.
No customer protection – If a pirate IPTV service disappears (which many do during crackdowns) or if a streaming link injects a virus, users have no recourse. There’s no refund, no support desk – you’re dealing with criminals, not companies. Additionally, accessing illegal streams could potentially lead to legal consequences for users in some jurisdictions (though enforcement usually targets suppliers).
To understand why piracy persists, it’s useful to compare the features of legitimate streaming platforms versus pirate streaming services (including illicit IPTV subscriptions and free streaming sites):
| Aspect | Legal Services | Pirate Services |
| Cost | $5–$15/month per platform |
Often free or ~$10/month for all content
|
| Content Access | Limited to licensed catalog |
Aggregates all platforms, no geo-restrictions
|
| Quality | HD/4K, reliable, ad-free |
Varies; risk of buffering, ads, or malware
|
| User Safety | Safe, secure payments, no legal risk |
Legal risk, fraud, and data/malware exposure
|
| Experience | Polished apps, support, personalized features |
Pop-ups, no support, UI often unstable or basic
|
Protecting Streams: Technical Countermeasures Against Streaming Piracy
Given the scale of streaming piracy, platforms are adopting layered defenses to deter content theft. While no method is foolproof, modern tools can drastically reduce piracy. Here’s a streamlined overview of the most effective techniques:
1. DRM Encryption: The First Line of Defense
Digital Rights Management (DRM) encrypts video files, ensuring playback only on authorized apps and devices. Netflix, Amazon, and VdoCipher use robust systems like Google Widevine, Apple FairPlay, and Microsoft PlayReady. Proper DRM:
- Prevents downloads via browser extensions or downloaders.
- Blocks playback on unauthorized or rooted devices.
- Stops screen recording on mobile with hardware-backed protection (Widevine L1).
With DRM, intercepted streams are unreadable without decryption keys, making piracy significantly harder.
2. Watermarking & Fingerprinting: Trace Every Leak
Watermarking embeds user identifiers (email, IP, ID) visibly or invisibly within the stream:
- Visible dynamic watermarking deters screen recording.
- Forensic watermarking is imperceptible but traceable if a leak occurs.
- Live broadcasters use session-specific watermarks to quickly identify pirating users.
VdoCipher enables customizable dynamic overlays, making every viewer accountable.
3. Access Control & Authentication
Platforms use strict controls to manage who can access what, including:
- Short-lived secure tokens tied to user sessions.
- Geo-restrictions for licensing compliance.
- Device, domain, and concurrent stream limits to prevent abuse.
- Blocking rooted/jailbroken devices and VPN/proxy usage.
VdoCipher offers domain locking and Play Integrity API integration to block high-risk devices.
4. Real-Time Monitoring & Takedowns
Even with protection in place, leaks happen. That’s where active monitoring steps in:
- Piracy detection via fingerprinting, web crawlers, and AI tools.
- DMCA takedown notices to remove illegal uploads.
- “War rooms” during live sports for real-time link removal.
- Coordination with ISPs, platforms (e.g. YouTube), and social media for instant disruption.
5. User Education and Better Alternatives
Consumers must be reminded:
- Pirate streams risk malware, fraud, and data theft.
- Illegal IPTV services often fund criminal operations.
To compete with pirates, legal services now offer, Flexible pricing, Bundled content and Ad-supported free tiers
VdoCipher: Hollywood-Grade Video Security for Premium Video Content
VdoCipher brings Hollywood-Grade Multi DRM protection to media companies, educators, and creators:
| Feature | Benefit | VdoCipher Implementation |
| Hollywood-Grade DRM | Encrypts content; blocks downloads & unauthorized playback |
Uses Google Widevine & Apple FairPlay DRM – same as Netflix & Amazon
|
| Dynamic Watermarking | Viewer-specific overlays deter leaks; aids traceability |
Real-time watermarking with user ID, IP, email; fully customizable in position & design
|
| Screen Record Blocking | Prevents screen recording on mobile apps and some desktop environments |
Disables recording on Android/iOS via SDK; enforces hardware-level DRM (L1)
|
| Device & Domain Locking | Limits playback to approved domains, devices, or apps |
Supports domain whitelisting, concurrent device control, and rooted/jailbroken blocking
|
| Geo & Token Restrictions | Restricts access by region or via time-limited stream URLs |
Implements secure playback tokens and geo/IP restrictions
|
| Analytics & Monitoring | Detects misuse like multi-IP logins or credential sharing |
Real-time usage logs, session tracking, IP detection, and abuse flagging
|
| VdoCipher Anti-Piracy Suite | All-in-one secure streaming + piracy deterrence tools for any content provider |
Full stack anti-piracy toolkit – secure player, watermarking, DRM, access control
|
Even small video businesses can now access studio-grade protection. By raising the piracy barrier, VdoCipher makes unauthorized redistribution costly and inconvenient, ensuring your revenue and IP stay secure.
FAQs
What is pirate streaming?
Pirate streaming refers to watching video content, movies, TV shows, or live events, through unauthorized websites or apps that do not hold legal distribution rights.
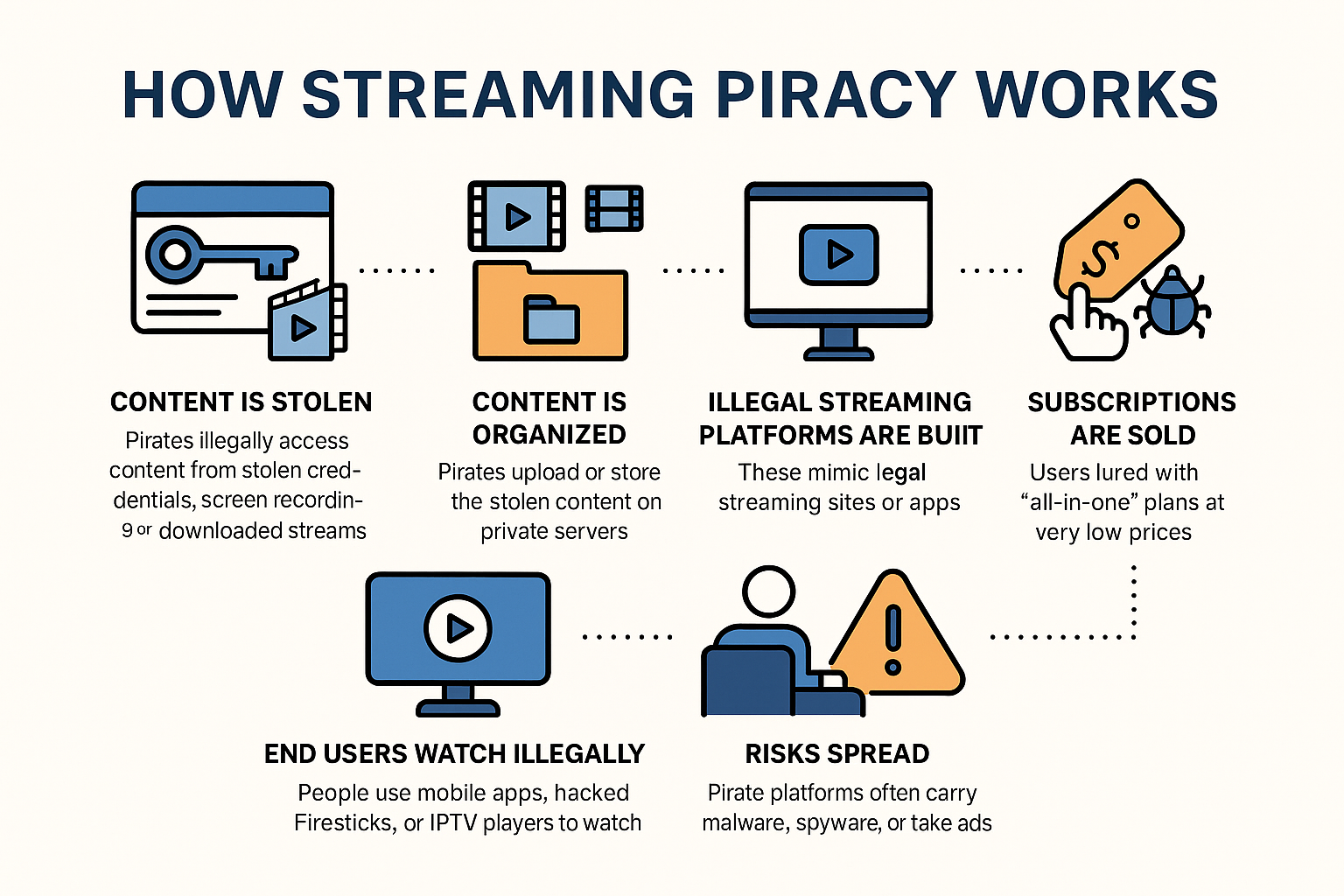
How does streaming piracy work?
Pirates steal live or on-demand content from legal platforms and redistribute it via illegal IPTV services, streaming sites, or apps, often profiting from ads or low-cost subscriptions.
Is streaming pirated content illegal?
Yes. Streaming pirated content is illegal in many countries and can lead to legal penalties, fines, and cybersecurity risks such as malware or data theft.
What are the risks of using pirated streaming services?
Users risk malware infections, phishing attacks, poor video quality, lack of customer support, and potential legal consequences for accessing illegal streams.
How do streaming platforms like Netflix fight piracy?
Platforms use DRM encryption, forensic watermarking, automated takedown tools, and legal actions, and they partner with anti-piracy coalitions to track and prosecute offenders.
What tools can smaller platforms use to stop streaming piracy?
Solutions such as VdoCipher provide Hollywood-grade DRM, dynamic watermarking, domain restrictions, and device authentication, enabling smaller platforms to secure their videos.
Why is streaming piracy increasing despite legal options?
Higher subscription costs, fragmented content across multiple services, and the convenience of low-cost pirate IPTV bundles drive more users toward pirated streaming sources.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.


Jyoti began her career as a software engineer in HCL with UNHCR as a client. She started evolving her technical and marketing skills to become a full-time Content Marketer at VdoCipher.

Leave a Reply